Lijun Zhu is a Ph.D. student of Electrical Engineering in Center for Energy and Geo-Processing (CEGP) at Georgia Institute of Technology. His research interests include detection and estimation in array processing, machine learning algorithm for seismic processing, and numerical modeling for seismic waves. Lijun is currently working on projects of event detection and localization of microseismics/micro-earthquakes using large surface dense array. He is one of the authors of the Seismic Simulation, Survey and Imaging (S3I) package between 2014 and 2016. He also actively contributing to open source packages, such as Obspy.
A resume is available here.
Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering (in progress), 2018
Georgia Institute of Technology
B.Sc. in Electrical Engineering, 2013
Georgia Institute of Technology
Jun 13, 2017, Meeting with seismology group at GT.
Apr 19, 2017, 2017 Annual Meeting, Seismological Society of America
Jun 2, 2016, 78th EAGE Conference & Exhibition 2016
Dec 15, 2015, The IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP)
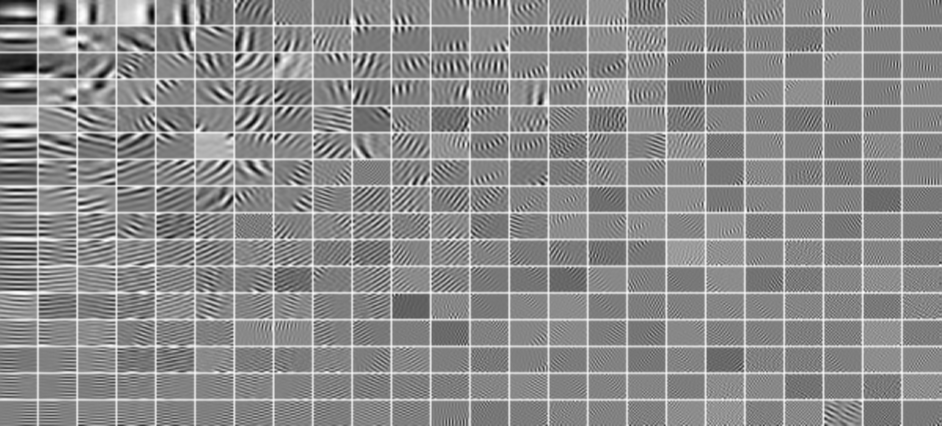
Noise is a never-ending problem for seismic processing due to the complex acquisition environment and loopn processing pipeline. This project tries to alleviate the noise challenge by looking at the intrinsic characteristic of siemsic signal. Signal correaltion and machine-learned dictionaries are studied to find the best space for signal-noise separation of targed seismic sections or images.

Over years, I like to join in field trips for seismic station deployment. These trips give me great opportutnities to make friends from different departments as well as get close to the nature. Along the way, I developed good skills for station deployment and seismic acquisition.
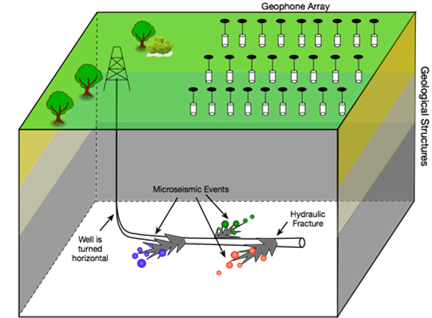
Surface microseismic offers a cheaper alternative to monitor hydraulic fracturing procees but is suffering the problem of severe background noise issue. This project tries to tackle the noise change through curve-fitting techniques and results in good performance for various applications.